The Advantages of Rapid Application Development (RAD)
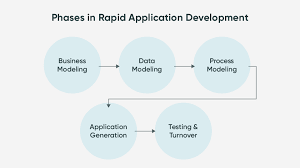
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a software development methodology that prioritises speed and flexibility in the application development process. Unlike traditional waterfall methods, RAD focuses on iterative development and prototyping to quickly produce high-quality applications tailored to user needs.
Key Features of RAD
RAD emphasises the following key features:
- Rapid Prototyping: RAD allows for the creation of prototypes that can be quickly reviewed and modified based on user feedback, leading to faster iterations.
- Iterative Development: The development process in RAD is iterative, with each iteration building upon the previous one, enabling continuous improvement and flexibility.
- User Involvement: Users play a crucial role in the RAD process by providing feedback early and frequently, ensuring that the final product meets their requirements.
- Collaboration: RAD promotes collaboration among cross-functional teams, including developers, designers, and users, fostering a more cohesive and efficient development environment.
- Flexibility: RAD allows for changes to be incorporated easily at any stage of development, accommodating evolving project requirements without significant delays.
The Benefits of RAD
RAD offers several advantages over traditional software development methodologies:
- Reduced Time-to-Market: By focusing on rapid iterations and prototyping, RAD accelerates the development process, allowing products to reach the market faster.
- Improved Quality: Continuous user feedback and testing throughout the development cycle result in higher-quality applications that better meet user expectations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The iterative nature of RAD helps identify issues early in the process, reducing rework costs and overall project expenses.
- Enhanced User Satisfaction: Involving users from the beginning ensures that their needs are met effectively, leading to increased user satisfaction with the final product.
- Faster Adaptation to Changes: RAD’s flexibility enables quick adjustments to changing requirements or market conditions without disrupting the development timeline significantly.
In conclusion, Rapid Application Development offers a dynamic approach to software development that prioritises speed, flexibility, and user involvement. By embracing RAD principles, organisations can streamline their development processes, deliver high-quality applications efficiently, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
8 Advantages of Rapid Application Development: Accelerating Time-to-Market and Enhancing Flexibility
- Faster time-to-market for applications
- Enhanced collaboration among development teams
- Continuous user feedback leads to improved user satisfaction
- Flexibility to accommodate changing requirements easily
- Cost-effective development process with reduced rework
- Higher-quality applications through iterative testing and refinement
- Increased adaptability to market changes and trends
- Efficient use of resources and quicker project delivery
Challenges of Rapid Application Development: Addressing Scalability, Complexity, User Dependency, and More
- Limited Scalability
- Complexity Management
- Dependency on User Availability
- Risk of Scope Creep
- Quality Assurance Concerns
- Resource Intensive
- Documentation Challenges
Faster time-to-market for applications
One of the key advantages of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is its ability to significantly reduce the time-to-market for applications. By prioritising rapid iterations, prototyping, and continuous user feedback, RAD enables developers to swiftly create and deploy high-quality applications in a timely manner. This accelerated development process allows businesses to introduce their products to the market quickly, gaining a competitive edge and meeting the ever-changing demands of customers efficiently.
Enhanced collaboration among development teams
Enhanced collaboration among development teams is a significant advantage of Rapid Application Development (RAD). By promoting close interaction and communication among developers, designers, and other stakeholders, RAD fosters a more cohesive and productive working environment. This collaborative approach ensures that team members can share ideas, feedback, and expertise effectively, leading to better coordination and alignment towards project goals. As a result, RAD enables development teams to work together seamlessly, leverage each other’s strengths, and collectively contribute to the successful delivery of high-quality applications within shorter timeframes.
Continuous user feedback leads to improved user satisfaction
Continuous user feedback is a significant advantage of Rapid Application Development (RAD) that directly contributes to enhanced user satisfaction. By involving users throughout the development process and gathering their feedback on prototypes and iterations, RAD ensures that the final product aligns with user expectations and needs. This iterative approach allows developers to address user concerns promptly, make necessary adjustments, and deliver a product that resonates with its intended audience. Ultimately, prioritising user feedback in RAD leads to higher levels of user satisfaction as the final application reflects users’ preferences and requirements more accurately.
Flexibility to accommodate changing requirements easily
One of the key advantages of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is its inherent flexibility to accommodate changing requirements easily. In traditional software development methodologies, adapting to evolving project needs can be challenging and time-consuming. However, RAD’s iterative approach allows for quick adjustments at any stage of development, ensuring that the final product aligns closely with the changing demands of users or market conditions. This flexibility not only enhances the responsiveness of development teams but also enables organisations to stay agile and effectively address shifting priorities without causing significant disruptions to the project timeline.
Cost-effective development process with reduced rework
One of the key advantages of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is its cost-effective development process with reduced rework. By focusing on iterative development and early user feedback, RAD helps identify and address issues at an early stage, minimising the need for extensive rework later in the development cycle. This proactive approach not only saves time but also reduces overall project expenses, making RAD an efficient and economical choice for organisations looking to streamline their software development processes.
Higher-quality applications through iterative testing and refinement
One of the key advantages of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is the ability to produce higher-quality applications through iterative testing and refinement. By incorporating continuous feedback loops and testing throughout the development process, RAD allows developers to identify and address issues early on, leading to improved functionality, usability, and overall quality of the final product. This iterative approach ensures that applications are thoroughly tested and refined, resulting in solutions that better meet user requirements and expectations.
Increased adaptability to market changes and trends
One of the key benefits of Rapid Application Development is its ability to enhance adaptability to market changes and trends. By embracing a flexible and iterative development approach, RAD enables organisations to quickly respond to evolving market demands, emerging trends, or shifting customer preferences. This agility allows businesses to stay ahead of the competition by efficiently incorporating changes into their applications, ensuring that their products remain relevant and competitive in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Efficient use of resources and quicker project delivery
One of the key advantages of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is its efficient use of resources and quicker project delivery. By focusing on iterative development and rapid prototyping, RAD enables teams to maximise resource allocation and streamline the development process, ultimately leading to faster project delivery times. This approach not only helps in reducing costs associated with prolonged development cycles but also ensures that projects are completed in a timely manner, allowing organisations to stay agile and responsive to market demands.
Limited Scalability
One notable drawback of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is its potential for limited scalability. Due to the emphasis on quick iterations and rapid prototyping, RAD projects may sometimes overlook the long-term scalability requirements of applications. This can lead to software that struggles to accommodate future growth or increased user demands, requiring substantial rework and modifications to ensure scalability. Organizations adopting RAD must carefully balance speed with scalability considerations to avoid potential challenges in accommodating future expansion and evolving business needs.
Complexity Management
In the context of Rapid Application Development (RAD), one significant drawback is Complexity Management. The iterative approach of RAD, while beneficial for quick iterations and user feedback, can result in a more intricate codebase. This increased complexity can make tasks such as maintenance and debugging more challenging for developers. As the code evolves rapidly through multiple iterations, ensuring the stability and scalability of the application becomes a greater concern, potentially leading to longer-term issues in managing and enhancing the software product.
Dependency on User Availability
Dependency on User Availability is a significant drawback of Rapid Application Development (RAD) methodology. The success of RAD hinges on consistent user involvement and timely feedback throughout the development cycle. However, if users are not readily available or lack engagement in the process, it can impede progress and lead to delays in project timelines. This dependency on user availability poses a challenge for RAD teams striving to deliver quick iterations and meet user requirements effectively.
Risk of Scope Creep
The flexibility inherent in Rapid Application Development (RAD) can inadvertently result in the challenge of scope creep. This phenomenon occurs when project requirements gradually expand beyond the initial scope, potentially affecting both timelines and budgets. The dynamic nature of RAD, while beneficial for accommodating changes, requires vigilant monitoring to prevent unchecked growth in project scope that could compromise the overall success of the development process.
Quality Assurance Concerns
Quality assurance concerns are a significant drawback of rapid application development. The emphasis on quick iterations and prototyping in RAD can sometimes lead to a compromise in thorough testing processes. This trade-off may result in overlooked bugs or performance issues within the application. Without comprehensive testing and quality assurance measures, the final product’s overall reliability and stability could be at risk, impacting user experience and satisfaction. It is essential for RAD teams to strike a balance between speed and quality to ensure that the end product meets the desired standards of functionality and performance.
Resource Intensive
One notable drawback of Rapid Application Development (RAD) is its resource-intensive nature. Implementing RAD effectively demands a dedicated team equipped with a range of skills to sustain the rapid pace of development. This can pose a challenge for certain organisations, as assembling and maintaining such a team may incur significant resources and expenses. The need for continuous collaboration and expertise across various domains in RAD projects can strain the resources of organisations that struggle to allocate the necessary manpower and expertise to support this accelerated development approach.
Documentation Challenges
In the realm of Rapid Application Development, one significant drawback revolves around documentation challenges. Owing to the rapid and iterative nature of RAD, there is a tendency for documentation tasks to take a back seat in priority. This can result in potential gaps in system comprehension and hinder effective knowledge transfer among team members. The lack of comprehensive documentation may pose obstacles in maintaining and scaling the application in the long run, highlighting the importance of striking a balance between speed and thorough documentation practices within RAD projects.
